Study guide for cellular respiration and photosynthesis – Delve into the captivating world of cellular respiration and photosynthesis with this comprehensive study guide. Prepare to unravel the intricate processes that sustain life on Earth, exploring the mechanisms that power cells and fuel the growth of plants.
This guide will lead you through a journey of discovery, shedding light on the fundamental principles, key players, and remarkable interplay between these two vital processes. Get ready to immerse yourself in the realm of cellular energy production and plant nutrition.
Cellular Respiration
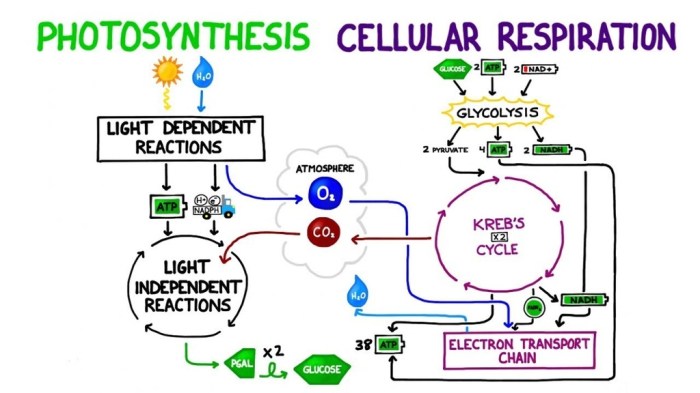
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that releases energy from organic compounds to provide energy for cells. It is essential for the survival of all living organisms, providing the energy needed for cellular processes, growth, and reproduction.
Cellular respiration occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Glycolysis
- Occurs in the cytoplasm
- Breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate
- Produces 2 molecules of ATP
- Releases 2 molecules of carbon dioxide
Krebs Cycle, Study guide for cellular respiration and photosynthesis
- Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
- Oxidizes pyruvate to carbon dioxide
- Produces 2 molecules of ATP
- Releases 6 molecules of carbon dioxide
Electron Transport Chain
- Occurs in the mitochondrial inner membrane
- Uses the energy released from the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 to pump protons across the membrane
- Produces 32-34 molecules of ATP
- Releases water as a byproduct
Cellular respiration can occur aerobically (with oxygen) or anaerobically (without oxygen).
Answers to Common Questions: Study Guide For Cellular Respiration And Photosynthesis
What is the primary role of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells generate energy in the form of ATP, the body’s primary energy currency.
How does photosynthesis differ from cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis utilizes light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, releasing oxygen as a byproduct, while cellular respiration breaks down glucose to release energy and produce carbon dioxide and water.
What is the significance of ATP in cellular processes?
ATP is the universal energy currency of cells, providing the energy required for various cellular activities, such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and nerve impulse transmission.

