The reference for analyzing any circuit is the current, a fundamental concept in electrical engineering that provides a comprehensive understanding of circuit behavior. This article delves into the principles of current analysis, exploring its role in deciphering the intricacies of electrical circuits.
Current, measured in amperes, quantifies the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is a crucial parameter for determining the behavior of circuit components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. By understanding current flow, engineers can design and analyze circuits efficiently, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Circuit Analysis Basics
Circuit analysis is the process of determining the electrical characteristics of a circuit, such as voltage, current, and power. It is a fundamental skill for electrical engineers and is used in a wide variety of applications, from designing new circuits to troubleshooting existing ones.
The reference for analyzing any circuit is the current. The current is the flow of electric charge, and it is measured in amperes (A). The voltage is the difference in electrical potential between two points in a circuit, and it is measured in volts (V).
The power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred, and it is measured in watts (W).
There are two main types of circuits: AC circuits and DC circuits. AC circuits are circuits in which the current and voltage vary over time, while DC circuits are circuits in which the current and voltage are constant.
Common circuit components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Resistors resist the flow of current, capacitors store electrical energy, and inductors oppose changes in current.
Kirchhoff’s Laws
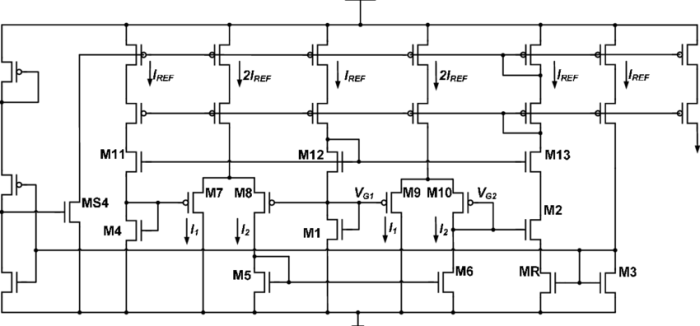
Kirchhoff’s laws are two fundamental laws that are used to analyze circuits. Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) states that the total current entering a node is equal to the total current leaving the node.
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) states that the sum of the voltages around a closed loop is equal to zero.
KCL and KVL can be used to solve a wide variety of circuit problems.
Circuit Analysis Techniques
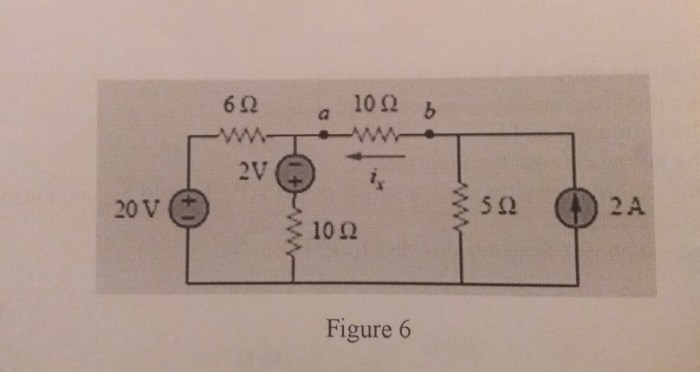
There are a number of different techniques that can be used to analyze circuits. Some of the most common techniques include:
- Nodal analysis
- Mesh analysis
- Superposition theorem
- Thevenin’s theorem
- Norton’s theorem
Each of these techniques has its own advantages and disadvantages. The best technique to use for a particular problem will depend on the specific circuit.
AC Circuit Analysis: The Reference For Analyzing Any Circuit Is The Current
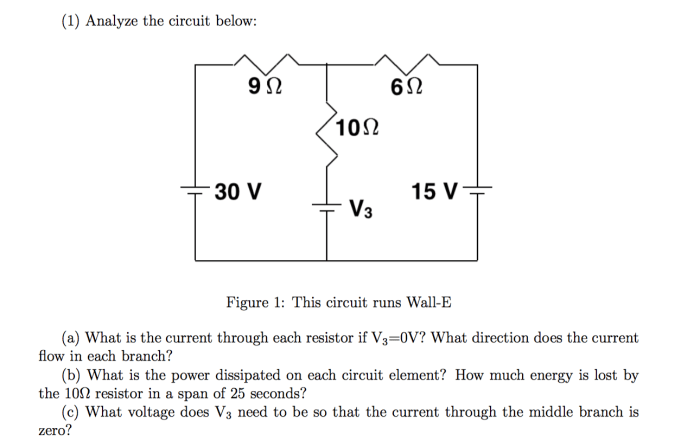
AC circuit analysis is the process of analyzing circuits that contain alternating current (AC). AC is a type of current that varies over time, and it is typically used in power transmission and distribution systems.
The concept of impedance is important in AC circuit analysis. Impedance is a measure of the opposition to the flow of AC current. It is measured in ohms (Ω).
There are a number of different types of AC circuits, including series circuits, parallel circuits, and resonant circuits.
Circuit Simulation and Software
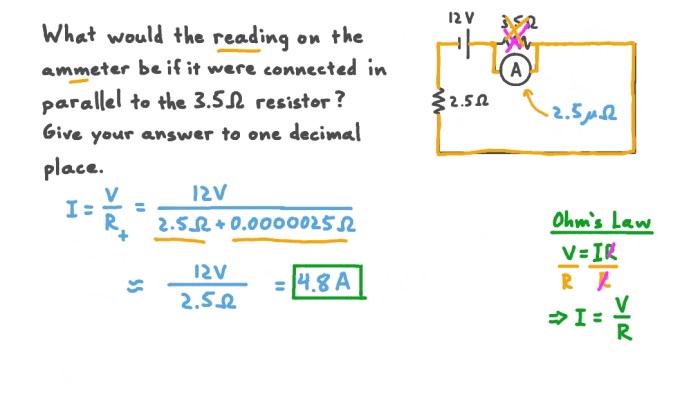
Circuit simulation software is a powerful tool that can be used to analyze circuits. Circuit simulation software allows users to create a virtual circuit and then simulate the circuit’s behavior.
There are a number of different circuit simulation software programs available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most popular circuit simulation software programs include:
- SPICE
- LTspice
- NI Multisim
- Cadence OrCAD
- Mentor Graphics PADS
Circuit simulation software can be used to analyze a wide variety of circuits, from simple circuits to complex circuits.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of current in circuit analysis?
Current is a fundamental parameter that quantifies the flow of electric charge, providing insights into the behavior of circuit components and enabling the design and analysis of electrical circuits.
How do Kirchhoff’s laws aid in circuit analysis?
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) are essential tools for analyzing circuits. KCL ensures that the total current entering a junction equals the total current leaving it, while KVL states that the algebraic sum of voltages around any closed loop in a circuit equals zero.
What are the different circuit analysis techniques?
Circuit analysis techniques include nodal analysis, mesh analysis, superposition theorem, Thevenin’s theorem, and Norton’s theorem. These techniques provide systematic approaches for solving complex circuit problems.